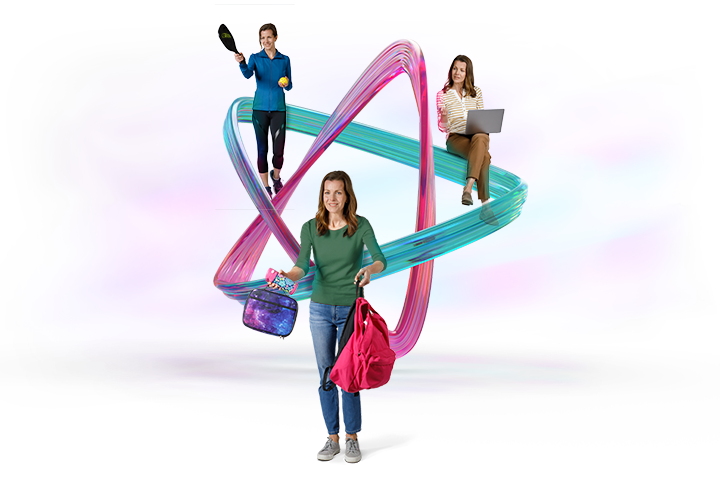
Are your patients ready to take control of a day full of ADHD challenges?
Consider AZSTARYS®—the FIRST and ONLY d‑MPH with novel SDX prodrug and IR activity1,2

AZSTARYS® is available for $60 or less for all commercially insured patients—see savings offer for eligible patients.

Rapid onset
of action, as fast as 30 minutes3,a
Sustained control throughout the day for up to 13 hours3,b
Smooth and gradual offset into the evening1,c
| a | Significant improvement vs placebo in PERMP-C scores as early as 30 minutes in lab classroom compared to baseline.3 |
| b | Significant improvement in mean change from baseline in SKAMP-C scores, averaged across 13-hour test day, compared to placebo in lab classroom.1,3 |
| c | Mean d-MPH plasma concentration time profile after single dose administration in healthy adults under fasted state.1 |

Select a profile
ADHD=attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; d-MPH=dexmethylphenidate; ER=extended-release; IR=immediate-release; PERMP-C=Permanent Product Measure of Performance-Correct; SDX=serdexmethylphenidate; SKAMP-C=Swanson, Kotkin, Agler, M-Flynn, and Pelham-Combined.
References: 1. AZSTARYS. Prescribing information. Corium LLC; 2025. 2. Mickle T, Guenther S, Chi G, inventors; KemPharm, Inc, assignee. Methylphenidate-prodrugs, processes of making and using the same. U.S. patent 10,584,113. March 10, 2020. 3. Kollins SH, Braeckman R, Guenther S, et al. A randomized, controlled laboratory classroom study of serdexmethylphenidate and d-methylphenidate capsules in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2021;31(9):597-609.
AZSTARYS is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in patients 6 years and older.
The use of AZSTARYS is not recommended in pediatric patients younger than 6 years of age because they had higher plasma exposure and a higher incidence of adverse reactions (e.g., weight loss) than patients 6 years and older at the same dosage.
WARNING: ABUSE, MISUSE, AND ADDICTION
AZSTARYS has a high potential for abuse and misuse, which can lead to the development of a substance use disorder, including addiction. Misuse and abuse of CNS stimulants, including AZSTARYS, can result in overdose and death and this risk is increased with higher doses or unapproved methods of administration, such as snorting or injection.
Before prescribing AZSTARYS, assess each patient’s risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction. Educate patients and their families about these risks, proper storage of the drug, and proper disposal of any unused drug. Throughout treatment, reassess each patient’s risk and frequently monitor for signs and symptoms of abuse, misuse, and addiction.
Please click here for Full
Prescribing Information,
including Boxed WARNING on Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction.

AZSTARYS is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in patients 6 years and older.
The use of AZSTARYS is not recommended in pediatric patients younger than 6 years of age because they had higher plasma exposure and a higher incidence of adverse reactions (e.g., weight loss) than patients 6 years and older at the same dosage.
WARNING: ABUSE, MISUSE, AND ADDICTION
AZSTARYS has a high potential for abuse and misuse, which can lead to the development of a substance use disorder, including addiction. Misuse and abuse of CNS stimulants, including AZSTARYS, can result in overdose and death and this risk is increased with higher doses or unapproved methods of administration, such as snorting or injection.
Before prescribing AZSTARYS, assess each patient’s risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction. Educate patients and their families about these risks, proper storage of the drug, and proper disposal of any unused drug. Throughout treatment, reassess each patient’s risk and frequently monitor for signs and symptoms of abuse, misuse, and addiction.
The site you're about to enter is intended for US healthcare professionals only.
By selecting OK to continue, you confirm you are a healthcare professional.